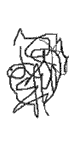
First disordered scribbles are simply records of enjoyable kinesthetic activity, not attempts at portraying the visual world. After six months of scribbling, marks are more orderly as children become more engrossed. Soon they begin to name scribbles, an important milestone in development.
Random scribbles begin at age one-and-a-half, but quite quickly take on definite shapes. Circular movement is first because it is most natural anatomically.
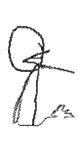
First conscious creation of form occurs around age three and provides a tangible record of the child’s thinking process. The first representational attempt is a person, usually with circle for head and two vertical lines for legs. Later other forms develop, clearly recognizable and often quite complex. Children continually search for new concepts so symbols constantly change.
After weeks of scribbling, children make the discovery of art: a drawn symbol can stand for a real thing in the environment. Circular form becomes a universal symbol for almost anything. Later symbols become more complex, reflecting child’s observations on the world around him.

First conscious creation of form occurs around age three and provides a tangible record of the child’s thinking process. The first representational attempt is a person, usually with circle for head and two vertical lines for legs. Later other forms develop, clearly recognizable and often quite complex. Children continually search for new concepts so symbols constantly change.
At four or five, the child begins to tell stories or work out problems with her drawings, changing basic forms as needed to express meaning. Often once the problem is expressed, the child feels better able to cope with it.
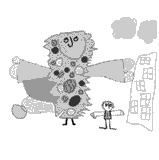
The child arrives at a “schema,” a definite way of portraying an object, although it will be modified when he needs to portray something important. The schema represents the child’s active knowledge of the subject. At this stage, there is definite order in space relationships: everything sits on the base line.
By five or six, children develop a set of symbols to create a landscape that eventually becomes a single variation repeated endlessly. A blue line and sun at the top of the page and a green line at the bottom become symbolic representations of the sky and ground. Landscapes are compose carefully, giving the impression that removing any single form would throw off the balance of the whole picture.
The child finds that schematic generalization no longer suffices to express reality. This dawning of how things really look is usually expressed with more detail for individual parts, but is far from naturalism in drawing. Space is discovered and depicted with overlapping objects in drawings and a horizon line rather than a base line. Children begin to compare their work and become more critical of it. While they are more independent of adults, they are more anxious to conform to their peers.
At nine or ten years, children try for more detail, hoping to achieve greater realism, a prized goal. Concern for where things are in their drawings is replaced by concern for how things look– particularly tanks, dinosaurs, super heroes, etc. for boys; models, horses, landscapes, etc. for girls.

The child finds that schematic generalization no longer suffices to express reality. This dawning of how things really look is usually expressed with more detail for individual parts, but is far from naturalism in drawing. Space is discovered and depicted with overlapping objects in drawings and a horizon line rather than a base line. Children begin to compare their work and become more critical of it. While they are more independent of adults, they are more anxious to conform to their peers.
The passion for realism is in full bloom. When drawings do not “come out right” (look real) they seek help to resolve conflict between how the subject looks and previously stored information that prevents their seeing the object as it really looks. Struggle with perspective, foreshortening, and similar spatial issues as they learn how to see.
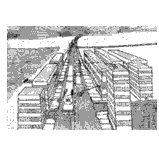
This stage marks the end of art as spontaneous activity as children are increasingly critical of their drawings. The focus is now on the end product as they strive to create “adult-like” naturalistic drawings. Light and shadow, folds, and motion are observed with mixed success, translated to paper. Space is depicted as three-dimensional by diminishing the size of objects that are further away.
The beginning of adolescence marks the end of artistic development among most children, due to frustration at “getting things right.” Those who do manage to weather the crisis and learn the “secret” of drawing will become absorbed in it. Edwards believes that proper teaching methods will help children learn to see and draw and prevent this crisis.

Art at this stage of life is something to be done or left alone. Natural development will cease unless a conscious decision is made to improve drawing skills. Students are critically aware of the immaturity of their drawing and are easily discouraged. Lowenfeld’s solution is to enlarge their concept of adult art to include non-representational art and art occupations besides painting (architecture, interior design, handcrafts, etc.)
_